Kubernetes ReplicaSet controller 详解
03 March 2020
与 ReplicationController 区别
- ReplicaSet 支持 Set-based requirement 和 Equality-based requirement 类型的 Label selectors,而 ReplicationController 只支持 Equality-based requirement 类型的 Label selectors
- ReplicaSet 会通过 ownerReference 接管 Pod,而 ReplicationController 只通过 Label selectors 接管 Pod。
创建与启动
- ctx.AvailableResources:可用的 GVR,由 cmd/kube-controller-manager/app.GetAvailableResources 通过 pkg/controller.SimpleControllerClientBuilder 创建的 client-go/kubernetes.Clientset 调用 kube-apiserver 的接口获得。
func startReplicaSetController(ctx ControllerContext) (http.Handler, bool, error) {
if !ctx.AvailableResources[schema.GroupVersionResource{Group: "apps", Version: "v1", Resource: "replicasets"}] {
return nil, false, nil
}
// 创建并启动控制器
go replicaset.NewReplicaSetController(
ctx.InformerFactory.Apps().V1().ReplicaSets(),
ctx.InformerFactory.Core().V1().Pods(),
ctx.ClientBuilder.ClientOrDie("replicaset-controller"),
replicaset.BurstReplicas,
).Run(int(ctx.ComponentConfig.ReplicaSetController.ConcurrentRSSyncs), ctx.Stop)
return nil, true, nil
}
创建
- eventBroadcaster:记录 ReplicaSet 处理时发生的一些事件,在 kubectl get events 和 kubectl describe 中可以看到
func NewReplicaSetController(rsInformer appsinformers.ReplicaSetInformer, podInformer coreinformers.PodInformer, kubeClient clientset.Interface, burstReplicas int) *ReplicaSetController {
eventBroadcaster := record.NewBroadcaster()
eventBroadcaster.StartLogging(klog.Infof)
eventBroadcaster.StartRecordingToSink(&v1core.EventSinkImpl{Interface: kubeClient.CoreV1().Events("")})
return NewBaseController(rsInformer, podInformer, kubeClient, burstReplicas,
apps.SchemeGroupVersion.WithKind("ReplicaSet"),
"replicaset_controller",
"replicaset",
controller.RealPodControl{
KubeClient: kubeClient,
Recorder: eventBroadcaster.NewRecorder(scheme.Scheme, v1.EventSource{Component: "replicaset-controller"}),
},
)
}
- burstReplicas:一次 sync 中创建/删除的 Pod 数量限制
- expectations:用于判断 rs 所期望的 Pod 的数量是否满足了
- queue:与 DeploymentController.queue 一样
func NewBaseController(rsInformer appsinformers.ReplicaSetInformer, podInformer coreinformers.PodInformer, kubeClient clientset.Interface, burstReplicas int,
gvk schema.GroupVersionKind, metricOwnerName, queueName string, podControl controller.PodControlInterface) *ReplicaSetController {
if kubeClient != nil && kubeClient.CoreV1().RESTClient().GetRateLimiter() != nil {
metrics.RegisterMetricAndTrackRateLimiterUsage(metricOwnerName, kubeClient.CoreV1().RESTClient().GetRateLimiter())
}
rsc := &ReplicaSetController{
GroupVersionKind: gvk,
kubeClient: kubeClient,
podControl: podControl,
burstReplicas: burstReplicas,
expectations: controller.NewUIDTrackingControllerExpectations(controller.NewControllerExpectations()),
queue: workqueue.NewNamedRateLimitingQueue(workqueue.DefaultControllerRateLimiter(), queueName),
}
rsInformer.Informer().AddEventHandler(cache.ResourceEventHandlerFuncs{
AddFunc: rsc.enqueueReplicaSet,
UpdateFunc: rsc.updateRS,
// This will enter the sync loop and no-op, because the replica set has been deleted from the store.
// Note that deleting a replica set immediately after scaling it to 0 will not work. The recommended
// way of achieving this is by performing a `stop` operation on the replica set.
DeleteFunc: rsc.enqueueReplicaSet,
})
rsc.rsLister = rsInformer.Lister()
rsc.rsListerSynced = rsInformer.Informer().HasSynced
podInformer.Informer().AddEventHandler(cache.ResourceEventHandlerFuncs{
AddFunc: rsc.addPod,
// This invokes the ReplicaSet for every pod change, eg: host assignment. Though this might seem like
// overkill the most frequent pod update is status, and the associated ReplicaSet will only list from
// local storage, so it should be ok.
UpdateFunc: rsc.updatePod,
DeleteFunc: rsc.deletePod,
})
rsc.podLister = podInformer.Lister()
rsc.podListerSynced = podInformer.Informer().HasSynced
rsc.syncHandler = rsc.syncReplicaSet
return rsc
}
启动
与 DeploymentController 类似。
// Run begins watching and syncing.
func (rsc *ReplicaSetController) Run(workers int, stopCh <-chan struct{}) {
// recover
defer utilruntime.HandleCrash()
// 关闭工作队列,停止所有 worker
defer rsc.queue.ShutDown()
controllerName := strings.ToLower(rsc.Kind)
klog.Infof("Starting %v controller", controllerName)
defer klog.Infof("Shutting down %v controller", controllerName)
// 等待 Lister 完成一遍同步
if !controller.WaitForCacheSync(rsc.Kind, stopCh, rsc.podListerSynced, rsc.rsListerSynced) {
return
}
// 启动指定数量的 worker 来处理资源对象变更
for i := 0; i < workers; i++ {
go wait.Until(rsc.worker, time.Second, stopCh)
}
// 等待控制器停止
<-stopCh
}
func (rsc *ReplicaSetController) worker() {
for rsc.processNextWorkItem() {
}
}
func (rsc *ReplicaSetController) processNextWorkItem() bool {
key, quit := rsc.queue.Get()
if quit {
return false
}
defer rsc.queue.Done(key)
err := rsc.syncHandler(key.(string))
if err == nil {
rsc.queue.Forget(key)
return true
}
// 处理出错,尝试重新入队
utilruntime.HandleError(fmt.Errorf("Sync %q failed with %v", key, err))
rsc.queue.AddRateLimited(key)
return true
}
控制循环流程图
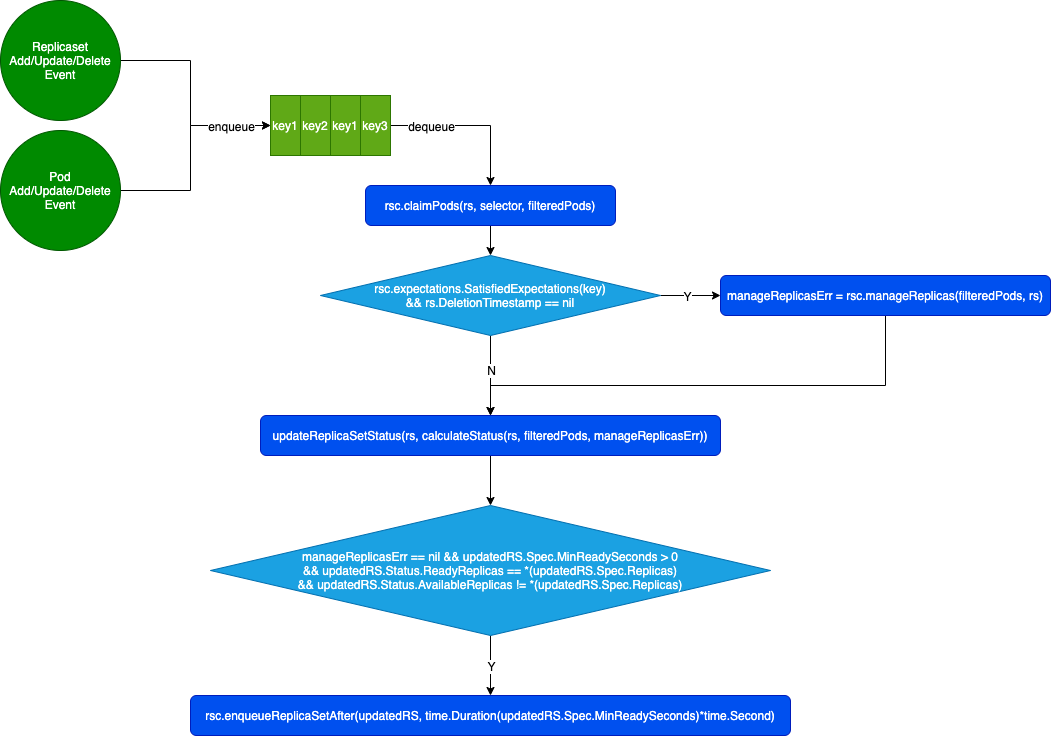
任务入队
发生以下事件时,会将 ReplicaSet 入队。
- ReplicaSet Add/Update/Delete:直接入队 RS
- addPod:如果 metav1.GetControllerOf(pod) != nil,则入队所属的 RS,并且调用 rsc.expectations.CreationObserved(rsKey)
- updatePod:
- 如果 curPod.ResourceVersion == oldPod.ResourceVersion,直接返回
- 如果 curPod.DeletionTimestamp != nil,调用 deletePod(curPod),返回
- 如果 Labels 发生修改,调用 deletePod(oldPod)
- 如果 controllerRef 发生修改,入队 oldPod 所属的 RS
- 如果 curControllerRef != nil,则入队 curPod 所属的 RS,返回
- 如果 !podutil.IsPodReady(oldPod) && podutil.IsPodReady(curPod) && rs.Spec.MinReadySeconds > 0 成立
- 那么在 rs.Spec.MinReadySeconds + 1 秒后,再次入队 curPod 所属的 RS,用于检查 Pod 的 ready 状态是否持续 rs.Spec.MinReadySeconds 秒
- 如果 !podutil.IsPodReady(oldPod) && podutil.IsPodReady(curPod) && rs.Spec.MinReadySeconds > 0 成立
- 这是一个孤儿 Pod,如果 labelChanged || controllerRefChanged 成立,找出所有 Label selectors 满足的 RSs 入队
任务出队,处理资源对象变更
- rsc.expectations.SatisfiedExpectations:判断 RS 期望创建/删除的 Pod 数量是否满足了
- controller.FilterActivePods:过滤出状态为 v1.PodSucceeded != p.Status.Phase && v1.PodFailed != p.Status.Phase && p.DeletionTimestamp == nil 的 Pod
- rsc.claimPods:遍历 filteredPods
- 找出 controllerRef.UID = rs.UID 的 Pod,如果 Label selectors 不匹配,则释放
- 找出 controllerRef.UID = nil 的 Pod,如果 Label selectors 匹配,则接管
- rsc.manageReplicas:如果 rsc.expectations.SatisfiedExpectations(key) && rs.DeletionTimestamp == nil,检查下是否还需要创建/删除 Pod
- diff = len(filteredPods) - rs.Spec.Replicas
- 如果 diff < 0,说明还需要创建 Pod
- creationCount = min(-diff, rsc.burstReplicas)
- rsc.expectations.ExpectCreations(rsKey, creationCount)
- slowStartBatch:批量创建 Pod,返回创建成功的 Pod 数量 successfulCreations
- skippedPods = creationCount - successfulCreations:需要从 expectations 减掉没有创建的 Pod 数量 rsc.expectations.CreationObserved(rsKey)
- 如果 diff > 0,说明还需要删除 Pod
- deletionCount = min(diff, rsc.burstReplicas)
- podsToDelete = getPodsToDelete(filteredPods, deletionCount):尽量删除不健康的 Pod
- rsc.expectations.ExpectDeletions(rsKey, getPodKeys(podsToDelete))
- 遍历 podsToDelete 逐个删除,并且更新 expectations:rsc.expectations.DeletionObserved(rsKey, podKey)
- 如果 diff < 0,说明还需要创建 Pod
- diff = len(filteredPods) - rs.Spec.Replicas
- calculateStatus:计算新的 rs.Status
- Replicas:len(filteredPods)
- FullyLabeledReplicas:pod.Labels 匹配 rs.Spec.Template.Labels 的 Pod 数量
- ReadyReplicas:GetPodCondition(pod.Status, v1.PodReady).Status == v1.ConditionTrue 的 Pod 数量
- AvailableReplicas:处于 Ready 状态,并且持续 rs.Spec.MinReadySeconds 时长的 Pod 数量
- rsc.enqueueReplicaSetAfter:延迟 updatedRS.Spec.MinReadySeconds 秒后把 rs 重新入队
func (rsc *ReplicaSetController) syncReplicaSet(key string) error {
startTime := time.Now()
defer func() {
klog.V(4).Infof("Finished syncing %v %q (%v)", rsc.Kind, key, time.Since(startTime))
}()
namespace, name, err := cache.SplitMetaNamespaceKey(key)
if err != nil {
return err
}
rs, err := rsc.rsLister.ReplicaSets(namespace).Get(name)
if errors.IsNotFound(err) {
klog.V(4).Infof("%v %v has been deleted", rsc.Kind, key)
rsc.expectations.DeleteExpectations(key)
return nil
}
if err != nil {
return err
}
rsNeedsSync := rsc.expectations.SatisfiedExpectations(key)
selector, err := metav1.LabelSelectorAsSelector(rs.Spec.Selector)
if err != nil {
utilruntime.HandleError(fmt.Errorf("Error converting pod selector to selector: %v", err))
return nil
}
// list all pods to include the pods that don't match the rs`s selector
// anymore but has the stale controller ref.
// TODO: Do the List and Filter in a single pass, or use an index.
allPods, err := rsc.podLister.Pods(rs.Namespace).List(labels.Everything())
if err != nil {
return err
}
// Ignore inactive pods.
filteredPods := controller.FilterActivePods(allPods)
// NOTE: filteredPods are pointing to objects from cache - if you need to
// modify them, you need to copy it first.
filteredPods, err = rsc.claimPods(rs, selector, filteredPods)
if err != nil {
return err
}
var manageReplicasErr error
if rsNeedsSync && rs.DeletionTimestamp == nil {
manageReplicasErr = rsc.manageReplicas(filteredPods, rs)
}
rs = rs.DeepCopy()
newStatus := calculateStatus(rs, filteredPods, manageReplicasErr)
// Always updates status as pods come up or die.
updatedRS, err := updateReplicaSetStatus(rsc.kubeClient.AppsV1().ReplicaSets(rs.Namespace), rs, newStatus)
if err != nil {
// Multiple things could lead to this update failing. Requeuing the replica set ensures
// Returning an error causes a requeue without forcing a hotloop
return err
}
// Resync the ReplicaSet after MinReadySeconds as a last line of defense to guard against clock-skew.
if manageReplicasErr == nil && updatedRS.Spec.MinReadySeconds > 0 &&
updatedRS.Status.ReadyReplicas == *(updatedRS.Spec.Replicas) &&
updatedRS.Status.AvailableReplicas != *(updatedRS.Spec.Replicas) {
rsc.enqueueReplicaSetAfter(updatedRS, time.Duration(updatedRS.Spec.MinReadySeconds)*time.Second)
}
return manageReplicasErr
}