golang memory
16 December 2019
参考文章:
Go 设计内存分配器,一是为了统一管理内存,提前分配或一次性释放大块内存,减少与操作系统进行系统调用造成的开销,进而提高程序的运行性能;二是为垃圾回收器提供支持。
传统意义上堆内存,被 Go 运行时划分为了两个部分:
- Go 运行时自身所需的堆内存
- Go 用户态代码和 goroutine 的执行栈所需的堆内存
整个内存分配器由数据结构 mheap 表示,如下图:
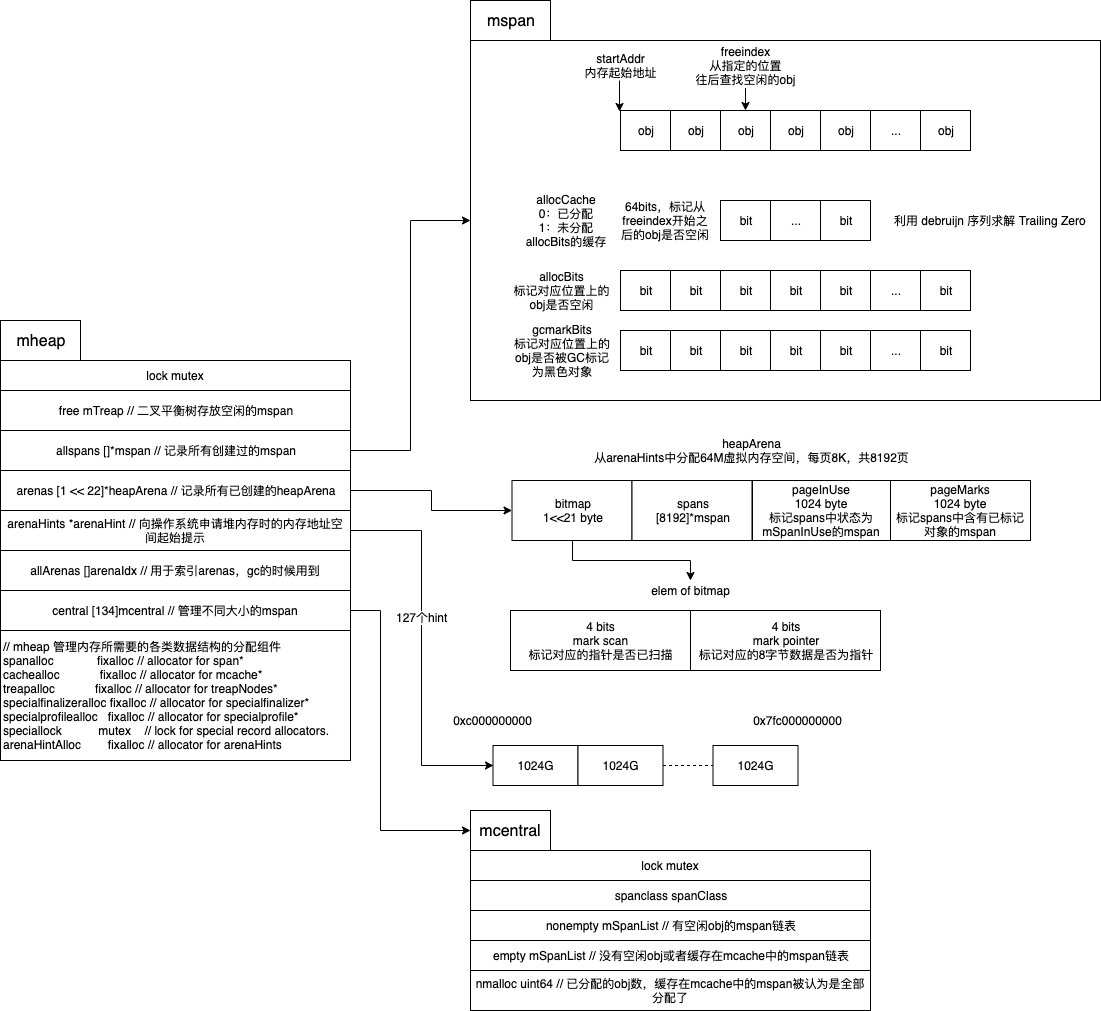
主要结构说明:
- heapArena:每个固定64M虚拟地址空间大小,如果分配的对象超过64M,则这个对象实际上占用的虚拟地址空间会跨多个 heapArena
- mspan:管理一连串的页,分配对象
- mcentral:收集指定大小等级的 mspan,提供给 mcache 用
- mcache:每个 P 的内存分配缓存
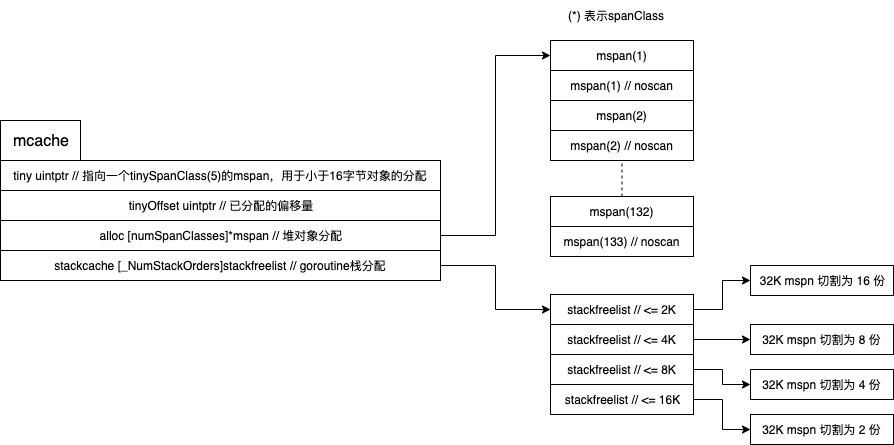
mcache 的结构如下图:
mspan 内存大小规格按对象大小定义在runtime/sizeclass.go中:
- class:类型编号
- bytes/obj:每个对象的大小
- bytes/span:该 mspan 占用的内存大小
- objects:该 mspan 有多少个对象可以分配
按照一定规格分类大小的对象管理内存,一是为了提高对象的复用率,二是为了方便内存管理
// class bytes/obj bytes/span objects tail waste max waste
// 1 8 8192 1024 0 87.50%
// 2 16 8192 512 0 43.75%
// 3 32 8192 256 0 46.88%
// 4 48 8192 170 32 31.52%
// 5 64 8192 128 0 23.44%
// 6 80 8192 102 32 19.07%
// 7 96 8192 85 32 15.95%
// 8 112 8192 73 16 13.56%
// 9 128 8192 64 0 11.72%
// 10 144 8192 56 128 11.82%
// 11 160 8192 51 32 9.73%
// 12 176 8192 46 96 9.59%
// 13 192 8192 42 128 9.25%
// 14 208 8192 39 80 8.12%
// 15 224 8192 36 128 8.15%
// 16 240 8192 34 32 6.62%
// 17 256 8192 32 0 5.86%
// 18 288 8192 28 128 12.16%
// 19 320 8192 25 192 11.80%
// 20 352 8192 23 96 9.88%
// 21 384 8192 21 128 9.51%
// 22 416 8192 19 288 10.71%
// 23 448 8192 18 128 8.37%
// 24 480 8192 17 32 6.82%
// 25 512 8192 16 0 6.05%
// 26 576 8192 14 128 12.33%
// 27 640 8192 12 512 15.48%
// 28 704 8192 11 448 13.93%
// 29 768 8192 10 512 13.94%
// 30 896 8192 9 128 15.52%
// 31 1024 8192 8 0 12.40%
// 32 1152 8192 7 128 12.41%
// 33 1280 8192 6 512 15.55%
// 34 1408 16384 11 896 14.00%
// 35 1536 8192 5 512 14.00%
// 36 1792 16384 9 256 15.57%
// 37 2048 8192 4 0 12.45%
// 38 2304 16384 7 256 12.46%
// 39 2688 8192 3 128 15.59%
// 40 3072 24576 8 0 12.47%
// 41 3200 16384 5 384 6.22%
// 42 3456 24576 7 384 8.83%
// 43 4096 8192 2 0 15.60%
// 44 4864 24576 5 256 16.65%
// 45 5376 16384 3 256 10.92%
// 46 6144 24576 4 0 12.48%
// 47 6528 32768 5 128 6.23%
// 48 6784 40960 6 256 4.36%
// 49 6912 49152 7 768 3.37%
// 50 8192 8192 1 0 15.61%
// 51 9472 57344 6 512 14.28%
// 52 9728 49152 5 512 3.64%
// 53 10240 40960 4 0 4.99%
// 54 10880 32768 3 128 6.24%
// 55 12288 24576 2 0 11.45%
// 56 13568 40960 3 256 9.99%
// 57 14336 57344 4 0 5.35%
// 58 16384 16384 1 0 12.49%
// 59 18432 73728 4 0 11.11%
// 60 19072 57344 3 128 3.57%
// 61 20480 40960 2 0 6.87%
// 62 21760 65536 3 256 6.25%
// 63 24576 24576 1 0 11.45%
// 64 27264 81920 3 128 10.00%
// 65 28672 57344 2 0 4.91%
// 66 32768 32768 1 0 12.50%
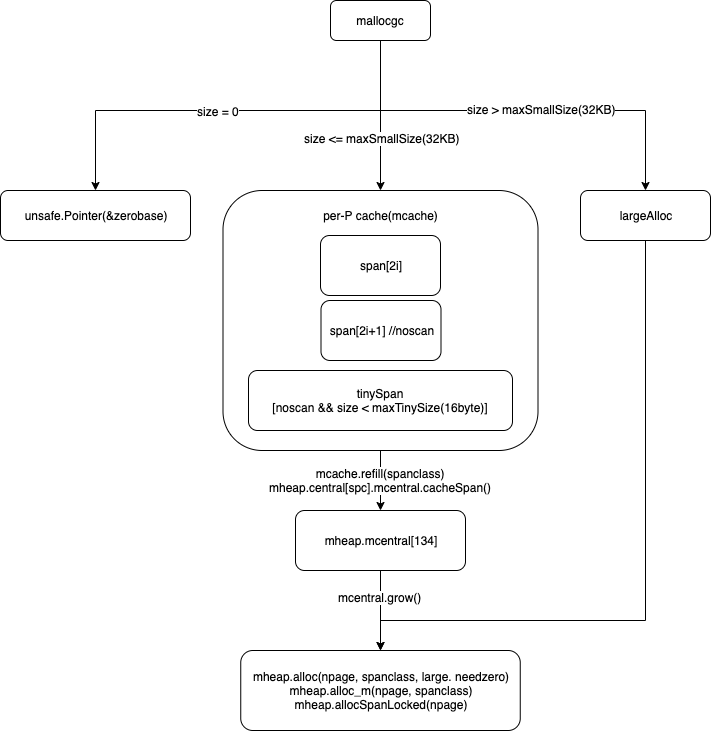
mspan 的分配
不管是 goroutine 运行时需要的栈内存或堆内存,都是通过 mspan 进行分配的,而 mspan 的分配则由func (h *mheap) allocSpanLocked(npage uintptr, stat *uint64) *mspan完成。
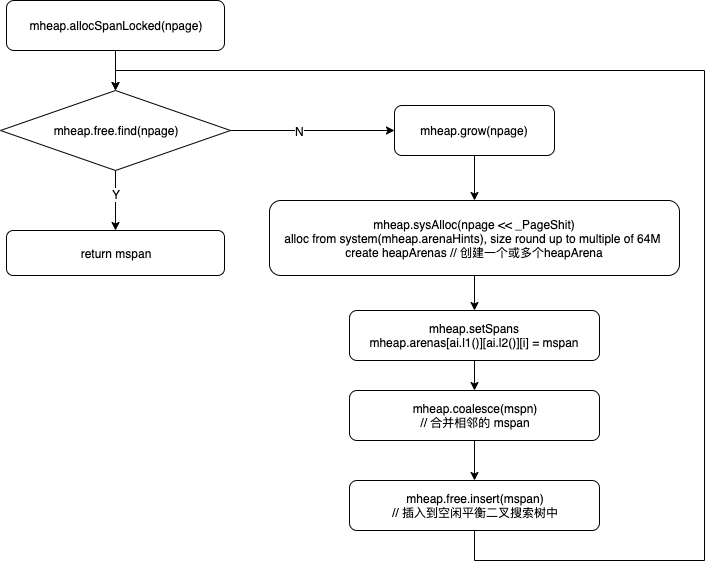
goroutine 栈内存的分配
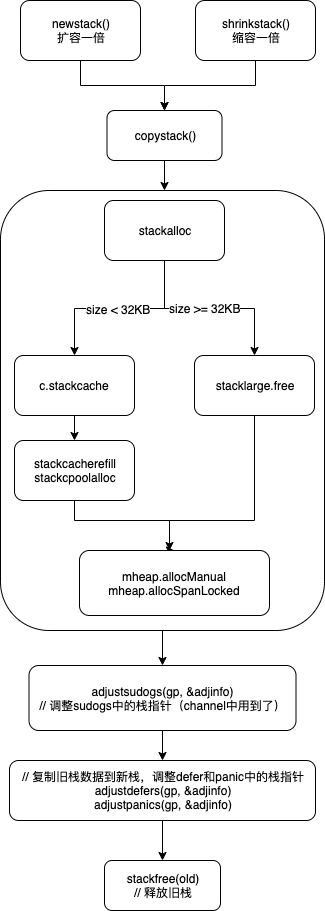
goroutine 堆内存的分配
mcache 分配对象分为3种情况:
- 小于16字节并且不需要扫描(不包含指针)的对象,从 tinySpan 中分配
- 不需要扫描(不包含指针)的对象,从 span[奇数索引] 中分配
- 需要扫描(包含指针)的对象,从 span[偶数索引] 中分配
内存统计
在用户代码中,我们可以通过runtime.ReadMemStats(m *MemStats)获取程序的内存统计信息,该过程需要 STW:
// ReadMemStats populates m with memory allocator statistics.
//
// The returned memory allocator statistics are up to date as of the
// call to ReadMemStats. This is in contrast with a heap profile,
// which is a snapshot as of the most recently completed garbage
// collection cycle.
func ReadMemStats(m *MemStats) {
stopTheWorld("read mem stats")
systemstack(func() {
readmemstats_m(m)
})
startTheWorld()
}
MemStats 结构体字段说明:
// A MemStats records statistics about the memory allocator.
type MemStats struct {
// General statistics.
// Alloc is bytes of allocated heap objects.
//
// This is the same as HeapAlloc (see below).
Alloc uint64 // 所有在使用的堆对象的字节数总和
// TotalAlloc is cumulative bytes allocated for heap objects.
//
// TotalAlloc increases as heap objects are allocated, but
// unlike Alloc and HeapAlloc, it does not decrease when
// objects are freed.
TotalAlloc uint64 // 所有分配堆对象的字节数总和
// Sys is the total bytes of memory obtained from the OS.
//
// Sys is the sum of the XSys fields below. Sys measures the
// virtual address space reserved by the Go runtime for the
// heap, stacks, and other internal data structures. It's
// likely that not all of the virtual address space is backed
// by physical memory at any given moment, though in general
// it all was at some point.
Sys uint64
// Lookups is the number of pointer lookups performed by the
// runtime.
//
// This is primarily useful for debugging runtime internals.
Lookups uint64
// Mallocs is the cumulative count of heap objects allocated.
// The number of live objects is Mallocs - Frees.
Mallocs uint64 // 总共分配了多少个堆对象
// Frees is the cumulative count of heap objects freed.
Frees uint64 // 总共释放了多少个堆对象
// Heap memory statistics.
//
// Interpreting the heap statistics requires some knowledge of
// how Go organizes memory. Go divides the virtual address
// space of the heap into "spans", which are contiguous
// regions of memory 8K or larger. A span may be in one of
// three states:
//
// An "idle" span contains no objects or other data. The
// physical memory backing an idle span can be released back
// to the OS (but the virtual address space never is), or it
// can be converted into an "in use" or "stack" span.
//
// An "in use" span contains at least one heap object and may
// have free space available to allocate more heap objects.
//
// A "stack" span is used for goroutine stacks. Stack spans
// are not considered part of the heap. A span can change
// between heap and stack memory; it is never used for both
// simultaneously.
// HeapAlloc is bytes of allocated heap objects.
//
// "Allocated" heap objects include all reachable objects, as
// well as unreachable objects that the garbage collector has
// not yet freed. Specifically, HeapAlloc increases as heap
// objects are allocated and decreases as the heap is swept
// and unreachable objects are freed. Sweeping occurs
// incrementally between GC cycles, so these two processes
// occur simultaneously, and as a result HeapAlloc tends to
// change smoothly (in contrast with the sawtooth that is
// typical of stop-the-world garbage collectors).
HeapAlloc uint64 // 所有在使用的堆对象的字节数总和
// HeapSys is bytes of heap memory obtained from the OS.
//
// HeapSys measures the amount of virtual address space
// reserved for the heap. This includes virtual address space
// that has been reserved but not yet used, which consumes no
// physical memory, but tends to be small, as well as virtual
// address space for which the physical memory has been
// returned to the OS after it became unused (see HeapReleased
// for a measure of the latter).
//
// HeapSys estimates the largest size the heap has had.
HeapSys uint64 // 内存管理器从系统申请的虚拟地址空间
// HeapIdle is bytes in idle (unused) spans.
//
// Idle spans have no objects in them. These spans could be
// (and may already have been) returned to the OS, or they can
// be reused for heap allocations, or they can be reused as
// stack memory.
//
// HeapIdle minus HeapReleased estimates the amount of memory
// that could be returned to the OS, but is being retained by
// the runtime so it can grow the heap without requesting more
// memory from the OS. If this difference is significantly
// larger than the heap size, it indicates there was a recent
// transient spike in live heap size.
HeapIdle uint64 // mheap.free中空闲的span总字节数
// HeapInuse is bytes in in-use spans.
//
// In-use spans have at least one object in them. These spans
// can only be used for other objects of roughly the same
// size.
//
// HeapInuse minus HeapAlloc estimates the amount of memory
// that has been dedicated to particular size classes, but is
// not currently being used. This is an upper bound on
// fragmentation, but in general this memory can be reused
// efficiently.
HeapInuse uint64 // 从mheap分配出去的span总字节数
// HeapReleased is bytes of physical memory returned to the OS.
//
// This counts heap memory from idle spans that was returned
// to the OS and has not yet been reacquired for the heap.
HeapReleased uint64 // 释放回操作系统的总字节数
// HeapObjects is the number of allocated heap objects.
//
// Like HeapAlloc, this increases as objects are allocated and
// decreases as the heap is swept and unreachable objects are
// freed.
HeapObjects uint64 // 有多少个对象正在使用
// Stack memory statistics.
//
// Stacks are not considered part of the heap, but the runtime
// can reuse a span of heap memory for stack memory, and
// vice-versa.
// StackInuse is bytes in stack spans.
//
// In-use stack spans have at least one stack in them. These
// spans can only be used for other stacks of the same size.
//
// There is no StackIdle because unused stack spans are
// returned to the heap (and hence counted toward HeapIdle).
StackInuse uint64 // goroutine 栈空间正在使用的字节总数
// StackSys is bytes of stack memory obtained from the OS.
//
// StackSys is StackInuse, plus any memory obtained directly
// from the OS for OS thread stacks (which should be minimal).
StackSys uint64 // 系统线程栈空间正在使用的字节总数 + StackInuse
// Off-heap memory statistics.
//
// The following statistics measure runtime-internal
// structures that are not allocated from heap memory (usually
// because they are part of implementing the heap). Unlike
// heap or stack memory, any memory allocated to these
// structures is dedicated to these structures.
//
// These are primarily useful for debugging runtime memory
// overheads.
// MSpanInuse is bytes of allocated mspan structures.
MSpanInuse uint64 // 正在使用的 numOf(mspan) * sizeOf(mspan)
// MSpanSys is bytes of memory obtained from the OS for mspan
// structures.
MSpanSys uint64 // 所有分配过的 numOf(mspan) * sizeOf(mspan)
// MCacheInuse is bytes of allocated mcache structures.
MCacheInuse uint64 // 正在使用的 numOf(mcache) * sizeOf(mcache)
// MCacheSys is bytes of memory obtained from the OS for
// mcache structures.
MCacheSys uint64 // 所有分配的 numOf(mcache) * sizeOf(mcache)
// BuckHashSys is bytes of memory in profiling bucket hash tables.
BuckHashSys uint64 // GC 和 mprof 使用的一些内存
// GCSys is bytes of memory in garbage collection metadata.
GCSys uint64 // GC 使用的一些内存
// OtherSys is bytes of memory in miscellaneous off-heap
// runtime allocations.
OtherSys uint64 // 运行时,调试和跟踪,以及内存管理器所需要的正在使用的内存
// Garbage collector statistics.
// NextGC is the target heap size of the next GC cycle.
//
// The garbage collector's goal is to keep HeapAlloc ≤ NextGC.
// At the end of each GC cycle, the target for the next cycle
// is computed based on the amount of reachable data and the
// value of GOGC.
NextGC uint64 // 下一次触发GC的堆内存上限
// LastGC is the time the last garbage collection finished, as
// nanoseconds since 1970 (the UNIX epoch).
LastGC uint64 // 上一次GC结束的时间点
// PauseTotalNs is the cumulative nanoseconds in GC
// stop-the-world pauses since the program started.
//
// During a stop-the-world pause, all goroutines are paused
// and only the garbage collector can run.
PauseTotalNs uint64 // 从程序启动到现在为止,GC STW总时间
// PauseNs is a circular buffer of recent GC stop-the-world
// pause times in nanoseconds.
//
// The most recent pause is at PauseNs[(NumGC+255)%256]. In
// general, PauseNs[N%256] records the time paused in the most
// recent N%256th GC cycle. There may be multiple pauses per
// GC cycle; this is the sum of all pauses during a cycle.
PauseNs [256]uint64 // 最近256次GC STW的时间
// PauseEnd is a circular buffer of recent GC pause end times,
// as nanoseconds since 1970 (the UNIX epoch).
//
// This buffer is filled the same way as PauseNs. There may be
// multiple pauses per GC cycle; this records the end of the
// last pause in a cycle.
PauseEnd [256]uint64 // 最近256次GC STW结束的时间点
// NumGC is the number of completed GC cycles.
NumGC uint32 // 总共执行了多少次GC
// NumForcedGC is the number of GC cycles that were forced by
// the application calling the GC function.
NumForcedGC uint32 // 总共由用户代码强制执行了多少次GC
// GCCPUFraction is the fraction of this program's available
// CPU time used by the GC since the program started.
//
// GCCPUFraction is expressed as a number between 0 and 1,
// where 0 means GC has consumed none of this program's CPU. A
// program's available CPU time is defined as the integral of
// GOMAXPROCS since the program started. That is, if
// GOMAXPROCS is 2 and a program has been running for 10
// seconds, its "available CPU" is 20 seconds. GCCPUFraction
// does not include CPU time used for write barrier activity.
//
// This is the same as the fraction of CPU reported by
// GODEBUG=gctrace=1.
GCCPUFraction float64 // GC 运行占用了多少 CPU 时间
// EnableGC indicates that GC is enabled. It is always true,
// even if GOGC=off.
EnableGC bool // 是否启用GC
// DebugGC is currently unused.
DebugGC bool
// BySize reports per-size class allocation statistics.
//
// BySize[N] gives statistics for allocations of size S where
// BySize[N-1].Size < S ≤ BySize[N].Size.
//
// This does not report allocations larger than BySize[60].Size.
BySize [61]struct { // 每种内存大小规格的mspan的使用情况统计
// Size is the maximum byte size of an object in this
// size class.
Size uint32 // mspan中的对象大小
// Mallocs is the cumulative count of heap objects
// allocated in this size class. The cumulative bytes
// of allocation is Size*Mallocs. The number of live
// objects in this size class is Mallocs - Frees.
Mallocs uint64 // mcentral分配出去的总对象数目 - mcentral回收的总对象数目 = mcache 拥有的总对象数目
// Frees is the cumulative count of heap objects freed
// in this size class.
Frees uint64 // mcache释放的总对象数目
}
}